
Using arcpy with aRcGeo
aRcGeo-arcpy-Examples.RmdIntroduction
This short vignette is meant to demonstrate the utility of working
with arcpy functions in the R environment. The following
will be a series of processing functions applied to a raster file.
Loading arcpy
In order to showcase some examples of arcpy functionality in R, we
will first need to import the python. This is where we will need to use
the aRcGeo::init_arcpy() function to import the module.
library(aRcGeo)
#> The functions in this library require the user to have `arcgisbinding` loaded.
#> Please load `library(arcgisbinding)` before running any aRcGeo functions.
init_arcpy(conda_env = "arcgispro-py3-DeepLearning")Using ArcGIS Pro’s Stretch and Segment functions
Importing Original Raster
We can import our original raster by using a file.path
function. In this case, the imported file is in a .tif
format.
Buchanan_Postal_Route_tif <- file.path(trim_path, "Postal_Routes_Selection.tif")An RGB render of this image looks like the following:
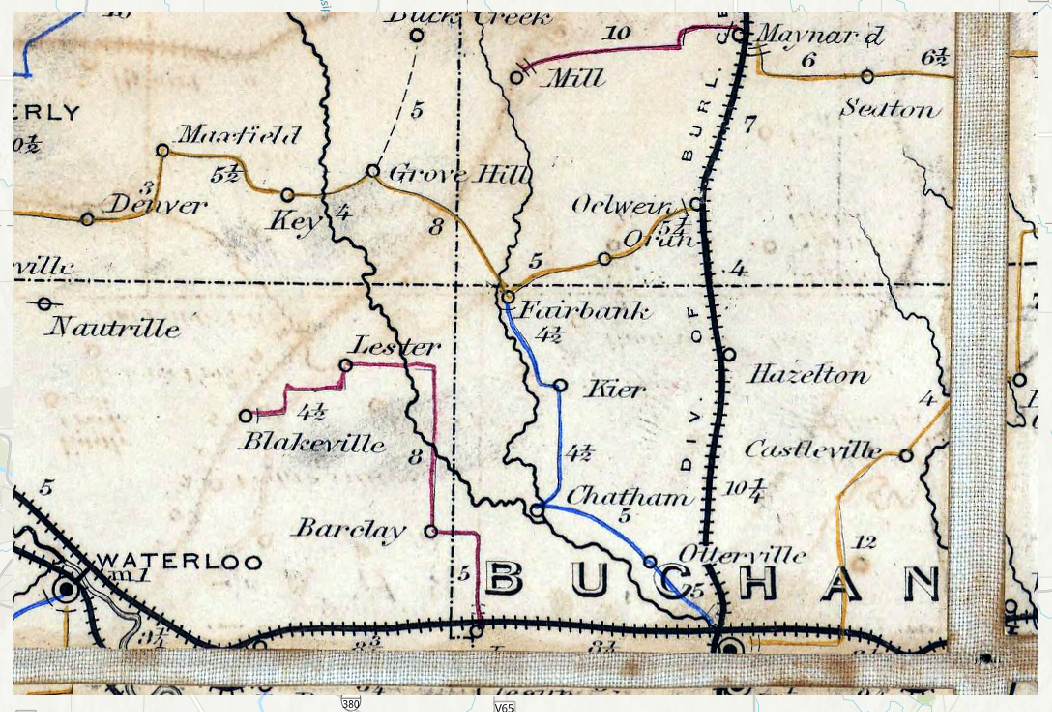
Buchanan Postal Routes Original
Stretched Raster
We would now like to use the stretch function in the
arcpy module to process the image. The following code
applies a Percentage Clipping stretch with a minimum percentage value of
0.05 and a maximum percentage value of 85. This will greatly reduce the
background noise of the image.
Stretched_Buchanan <- arcpy$ia$Stretch(Buchanan_Postal_Route_tif,
stretch_type ="PercentClip",
min_percent = 0.05,
max_percent = 85)
Stretched_Buchanan$save("Stretched Buchanan")Our processed image now looks like the following:
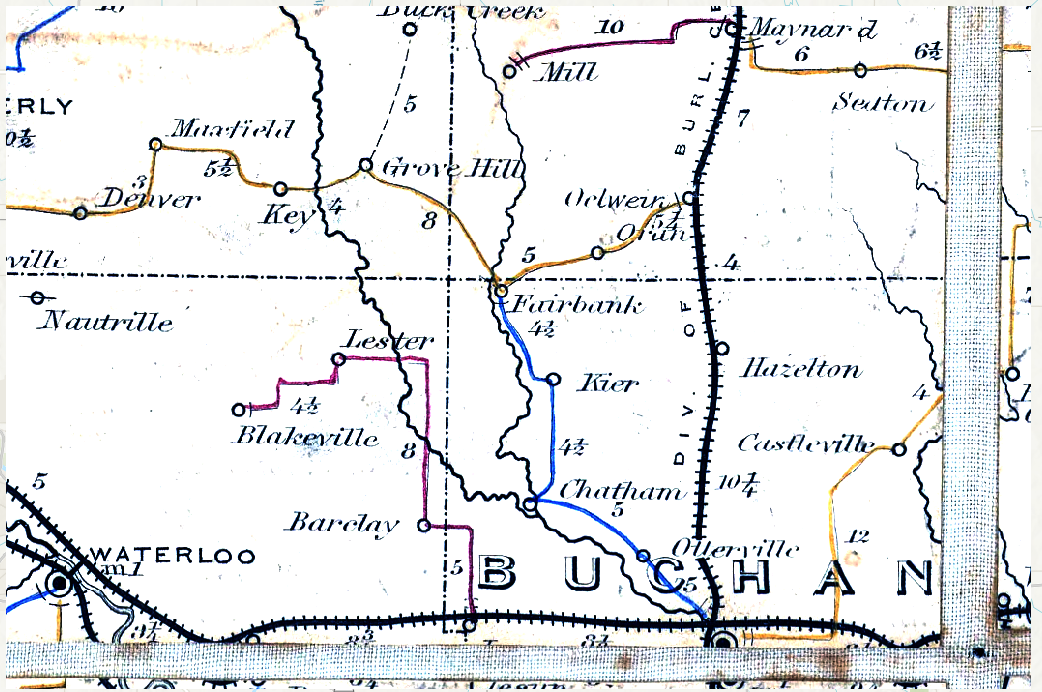
Buchanan Postal Routes Stretched
Segmented Raster
Once the stretched image process is complete, the raster will also go through a segmentation process which we can call in the following function.
Segmented_Buchanan <- arcpy$sa$SegmentMeanShift(in_raster = Stretched_Buchanan,
spectral_detail = 5,
spatial_detail = 15)
Segmented_Buchanan$save("Segmented Buchanan")The applied segmentation function from the arcpy module
has inputs of detail on a scale from 0-20. The following image is the
output of a high spatial and low spectral segmented image.
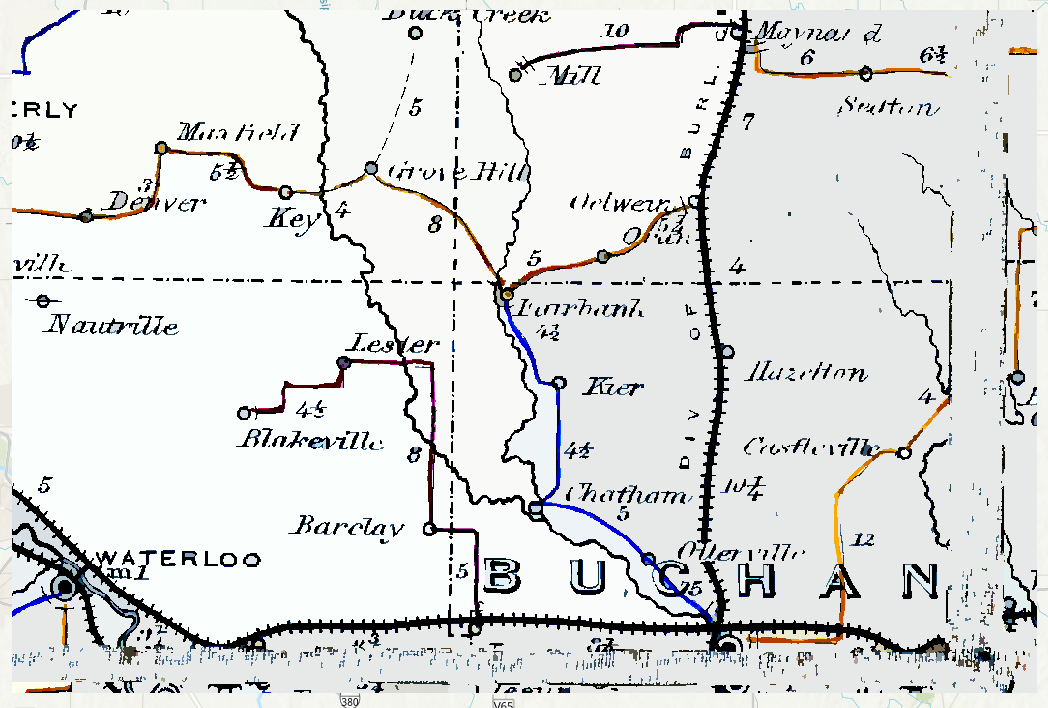
Buchanan Postal Routes Segmented
Discussion
As the examples demonstrate, arcpy functionality is
possible in R using R syntax to execute Python functions in R code
chunks rather than having to call scripts. R is also able to recognize
ESRI spatial objects, making conversions and compatibility with other
R-spatial packages a possibility.